This is the multi-page printable view of this section. Click here to print.
Installation and Deployment
- 1: CSI
- 1.1: Installation Preparations
- 1.1.1: Downloading the Huawei CSI Software Package
- 1.1.2: Uploading a Huawei CSI Image
- 1.1.3: Checking User Configurations on Huawei Storage
- 1.1.4: Checking Volume Snapshot-Dependent Components
- 1.1.5: Checking the Host Multipathing Configuration
- 1.1.6: Checking the Status of Host-Dependent Software
- 1.1.7: Checking the Images on Which CSI Depends
- 1.2: Installation
- 1.2.1: Installation Using Helm
- 1.2.1.1: Installing Huawei CSI on Kubernetes, OpenShift, and Tanzu
- 1.2.1.2: Installing Huawei CSI on the CCE or CCE Agile Platform
- 1.2.1.3: Parameters in the values.yaml File of Helm
- 1.2.2: Manual Installation
- 1.3: Uninstallation
- 1.3.1: Uninstallation Using Helm
- 1.3.1.1: Uninstalling Huawei CSI on Kubernetes, OpenShift, and Tanzu
- 1.3.1.2: Uninstalling Huawei CSI on CCE or CCE Agile
- 1.3.1.3: Uninstalling CSI-Dependent Component Services
- 1.3.2: Manual Uninstallation
- 1.4: Upgrade
- 1.4.1: Upgrade Using Helm
- 1.4.1.1: Upgrading from 2.x or 3.x to 4.x
- 1.4.1.2: Upgrading Huawei CSI on Kubernetes, OpenShift, and Tanzu
- 1.4.1.3: Upgrading Huawei CSI on CCE or CCE Agile
- 1.4.2: Manual Upgrade
- 1.5: Rollback
1 - CSI
1.1 - Installation Preparations
This chapter describes the preparations for the installation.
Prerequisites
- The container management platform has been deployed and is running properly. The container platform compatibility requirements in Compatibility and Features are met.
- (Mandatory for enterprise storage) Initial configuration for interconnecting with Huawei enterprise storage has been completed, including storage pool division and port configuration. The version of the storage product meets the requirements in Compatibility and Features .
- (Mandatory for distributed storage) Initial configuration for interconnecting with Huawei distributed storage has been completed, including storage pool division and port configuration. The version of the storage product meets the requirements in Compatibility and Features .
- The connectivity between Huawei storage and the container platform host has been configured. For example, the worker node running huawei-csi-controller communicates properly with the management IP address of the storage device to be connected, and the worker node running huawei-csi-node communicates properly with the service IP address of the storage device to be connected. In iSCSI scenarios, the ping command can be used to verify the connectivity.
- Ensure that the language of the operating system is English.
- Ensure that storage resource names, such as storage pool names and tenant names, are in English.
1.1.1 - Downloading the Huawei CSI Software Package
This section describes how to download the software package and the component structure of the software package.
Open a browser and enter https://github.com/Huawei/eSDK_K8S_Plugin/releases in the address box.
Download the software package of the 4.10.0 version based on the CPU architecture.

- Software package naming rule: Plug-in name (eSDK_Storage_CSI) + Version number + CPU architecture
- CSI supports the following CPU architectures: x86, Arm, and PPC64LE.
Decompress the downloaded software package. The following table shows the component structure of the software package.
Table 1 Component description
1.1.2 - Uploading a Huawei CSI Image
Huawei provides the huawei-csi image for users. For details about how to obtain the image file, see Downloading the Huawei CSI Software Package .
To use the CSI image on the container management platform, you need to import the CSI image to the cluster in advance:
- Method 1: (Recommended) Use Docker to upload the CSI image to the image repository. For details, see Uploading an Image to the Image Repository .
- Method 2: Manually import the CSI image to all nodes where Huawei CSI needs to be deployed. For details, see Uploading an Image to a Local Node .
Uploading an Image to the Image Repository
The installation of Huawei CSI depends on the following image files provided by Huawei. Import and upload the image files in sequence. For details about how to obtain the image files, see Downloading the Huawei CSI Software Package .
- huawei-csi-v4.10.0-arch.tar
- storage-backend-controller-v4.10.0-arch.tar
- storage-backend-sidecar-v4.10.0-arch.tar
- huawei-csi-extender-v4.10.0-arch.tar
Prerequisites
A Linux host with Docker installed is available, and the host can access the image repository.
Procedure
Run the following command to import the CSI image to the current node. arch indicates the CPU architecture.
docker load -i huawei-csi-v4.10.0-<arch>.tarRun the following command to add the image repository address to the image tag. repo.huawei.com indicates the image repository address.
docker tag huawei-csi:4.10.0 <repo.huawei.com>/huawei-csi:4.10.0Run the following command to upload the CSI image to the image repository. repo.huawei.com indicates the image repository address.
docker push <repo.huawei.com>/huawei-csi:4.10.0
- Run the corresponding CLI command to load and push the image based on the container runtime environment (for example, Docker or Containerd).
- For details about how to import and upload images to the CCE or CCE Agile platform, see the user manual of the platform.
Uploading an Image to a Local Node
If the image has been uploaded to the image repository, skip this section.
Prerequisites
- The node has the corresponding Huawei CSI image file. For details about how to obtain the image file, see Downloading the Huawei CSI Software Package .
- Docker or another container engine has been installed on the node.
Procedure
- Use a remote access tool, such as PuTTY, to log in to the node where the image is to be imported through the management IP address.
- Copy the image directory in the Kubernetes CSI component package to any directory on the current node.
- Run the cd image command to go to the image working directory. For details about the tool path, see Table 1 .
- Run the following commands in sequence to import all Huawei CSI images in the image directory to the local node. In the commands, name indicates the name of a .tar image package.
Run the following command using the Docker container engine:
docker load -i <name>.tarRun the following command using the containerd container engine:
ctr -n k8s.io image import <name>.tarRun the following command using the Podman container engine:
podman load -i <name>.tar
If another container engine is installed on the node, use the image import command for the corresponding container engine.
1.1.3 - Checking User Configurations on Huawei Storage
After Huawei storage is connected to the container platform, Huawei CSI needs to manage storage resources on Huawei storage based on service requirements, such as creating and mapping volumes. In this case, Huawei CSI needs to use the users created on Huawei storage to communicate with Huawei storage. The following table lists the user information required for different storage devices.
Table 1 User requirements for connecting storage to CSI
- If a user-defined role is used, you need to configure permissions for the role. For details about how to configure the minimum permissions, see Configuring Custom Permissions .
- If the LDAP authentication mode is used, you need to set the authenticationMode parameter when creating a backend. For details, see the parameter description in Configuring the Storage Backend .
- Based on the principle of minimum and system security requirements, users under the super administrator role are not recommended.
1.1.4 - Checking Volume Snapshot-Dependent Components
This section describes how to check the volume snapshot-dependent components in the cluster.
If Huawei CSI is deployed in a version earlier than Kubernetes v1.20, perform the following steps:
Run the following command to check the Kubernetes version. The following uses Kubernetes v1.16.0 as an example.
kubectl get nodeThe following is an example of the command output.
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION test-master Ready master 311d v1.16.0 test-node Ready <none> 311d v1.16.0Copy the helm directory in the Kubernetes CSI component package to any directory on the master node. For details about the Helm tool path, see Table 1 .
Go to the helm/esdk/crds/snapshot-crds directory and run the following command to delete the snapshot CRD installation file.
rm -rf ./huawei-csi-snapshot-crd-v1.yaml
1.1.5 - Checking the Host Multipathing Configuration
If you plan to use the FC/iSCSI/NVMe over RoCE/NVMe over FC protocol to access Huawei storage in a container environment, you are advised to use host multipathing software to enhance the link redundancy and performance of the host and storage. If you do not want to use the software, skip this section.
For details about the OSs and multipathing software that can be interconnected with Huawei CSI software, see the OS compatibility in Compatibility and Features .
- If you want to use the FC/iSCSI protocol to connect to Huawei storage, you are advised to use native DM-Multipath provided by the OS.
- If you want to use the NVMe over RoCE/NVMe over FC protocol to connect to Huawei storage, you are advised to use Huawei-developed UltraPath-NVMe.
- If you want to use the SCSI protocol to connect to Huawei storage, disable DM-Multipath provided by the OS.
Prerequisites
Multipathing software has been correctly installed on a host.
- If you use native DM-Multipath provided by the OS, contact your host or OS provider to obtain the documents and software packages required for the installation.
- If you use Huawei-developed UltraPath or UltraPath-NVMe, contact Huawei engineers to obtain the UltraPath or UltraPath-NVMe documents and software packages. For details about the software package version, see the OS compatibility in Compatibility and Features .
Procedure
If you use the iSCSI/FC protocol to connect to Huawei enterprise storage, configure and check host multipathing by referring to OceanStor Dorado and OceanStor Host Connectivity Guide for Red Hat .
If you use the NVMe over RoCE/NVMe over FC protocol to connect to Huawei enterprise storage, configure and check host multipathing by referring to OceanStor Dorado and OceanStor Host Connectivity Guide for Red Hat .
If you use iSCSI to connect to Huawei distributed storage, configure and check host multipathing by referring to Configuring Multipathing for an Application Server in FusionStorage 8.0.1 Block Storage Basic Service Configuration Guide
If you use the native multipathing software provided by the OS, check whether the /etc/multipath.conf file contains the following configuration item.
defaults { user_friendly_names yes find_multipaths no }If the configuration item does not exist, add it to the beginning of the /etc/multipath.conf file.

For details about the functions of the user_friendly_names and find_multipaths parameters, see dm_multipath/config_file_defaults .
1.1.6 - Checking the Status of Host-Dependent Software
This section describes how to check whether the status of host-dependent software on worker nodes in a cluster is normal. In this example, the host OS is CentOS 7.9 x86_64.
Check the status of the iSCSI client.
systemctl status iscsi iscsidCheck the status of the NFS client.
systemctl status rpcbindCheck the status of DM-Multipath.
systemctl status multipathd.socket multipathdCheck the status of UltraPath.
systemctl status nxupCheck the status of UltraPath-NVMe.
systemctl status upudev upService_plusCheck the status of the DataTurbo client. For details, see OceanStor DataTurbo 25.1.0 DTFS User Guide .
Check the status of the NFS+ client. For details, see NFS+ Client 1.x User Guide .
1.1.7 - Checking the Images on Which CSI Depends
The installation of Huawei CSI depends on the images listed in the following table. If all worker nodes in the cluster have been connected to the Internet and can pull images online, you can skip this section. If nodes in the cluster cannot connect to the Internet, download the corresponding image file based on the Kubernetes version and upload it to the image repository or import it to all worker nodes in the Kubernetes cluster.
The huawei-csi-controller service depends on the following sidecar images: livenessprobe, csi-provisioner, csi-attacher, csi-resizer, csi-snapshotter, snapshot-controller, storage-backend-controller, storage-backend-sidecar, huawei-csi-driver, and huawei-csi-extender. The huawei-csi-node service depends on the following sidecar images: livenessprobe, csi-node-driver-registrar, and huawei-csi-driver.
For details about the functions and details of each image, see the following table.
Table 1 Images on which Huawei CSI depends
If the cluster is not connected to the Internet, manually download the container images and upload them to the cluster. For details, see Downloading a Container Image .
1.2 - Installation
This section describes how to install Huawei CSI.
In the current version, resource requests and limits are added to Huawei CSI. For details, see Huawei CSI Resource Management .
Prerequisites
- Operations described in Installation Preparations have been completed.
- All worker nodes of the cluster communicate properly with the service network of the storage device to be connected. In iSCSI scenarios, the ping command can be used to verify the connectivity.
- Software clients required by the corresponding protocol, such as iSCSI and NFS clients, have been installed on all worker nodes of the cluster.
1.2.1 - Installation Using Helm
This section describes how to install Huawei CSI using Helm 3.
Helm Installation Description
- Huawei CSI can be installed as the root user or a non-root user. When installing Huawei CSI as a non-root user, ensure that the current user can access the API Server of the Kubernetes cluster. For details about how to configure access to the Kubernetes cluster as a non-root user, see Configuring Access to the Kubernetes Cluster as a Non-root User .
- Huawei CSI must be run as the root user.
Helm is a software package management tool in the Kubernetes ecosystem. Similar to Ubuntu APT, CentOS YUM, or Python pip, Helm manages Kubernetes application resources.
You can use Helm to package, distribute, install, upgrade, and roll back Kubernetes applications in a unified manner.
- For details about how to obtain and install Helm, see https://helm.sh/docs/intro/install/ .
- For details about the mapping between Helm and Kubernetes versions, see https://helm.sh/docs/topics/version_skew/ .
When installing huawei-csi-controller, Helm deploys the following components in the workloads of the Deployment type in the specified namespace:
- huawei-csi-driver: Huawei CSI driver.
- storage-backend-controller: Huawei backend management controller, used to manage storageBackendClaim resources.
- storage-backend-sidecar: used to manage storageBackendContent resources.
- Kubernetes External Provisioner: used to provide or delete volumes.
- Kubernetes External Attacher: used to attach or detach volumes.
- Kubernetes External Resizer: used to expand the capacity of volumes.
- Kubernetes External liveness-probe: used to determine the health status of a Pod.
- (Optional) huawei-csi-extender: Huawei CSI extender.
- (Optional) Kubernetes External Snapshotter: used to provide snapshot support (installed as CRD).
- (Optional) Kubernetes External Snapshot Controller: used to control volume snapshots.
When installing huawei-csi-node, Helm deploys the following components in the workloads of the DaemonSet type in the specified namespace:
- huawei-csi-driver: Huawei CSI driver.
- Kubernetes Node Registrar: used to process driver registration.
- liveness-probe: used to determine the health status of a Pod.
1.2.1.1 - Installing Huawei CSI on Kubernetes, OpenShift, and Tanzu
Installation Procedure
Use a remote access tool, such as PuTTY, to log in to any master node in the cluster through the management IP address.
Copy the helm directory in the Kubernetes CSI component package to any directory on the master node. For details about the Helm tool path, see Table 1 .
Go to the helm/esdk working directory.
cd helm/esdkPrepare the values.yaml file. Huawei CSI provides the values.yaml template file in the helm/esdk directory of the software package. You can also modify parameters according to Parameters in the values.yaml File of Helm to customize Huawei CSI.
Perform the following configuration before the installation:
- If the container platform is Kubernetes, skip this step.
- If the container platform is OpenShift, perform the configuration in Installation and Configuration on the OpenShift Platform .
- If the container platform is Tanzu, perform the configuration in Installation and Configuration on the Tanzu Platform .
Run the following command to update the storage backend CRD.
kubectl apply -f ./crds/backend/(Optional) Check snapshot-dependent components by following the instructions provided in Checking Volume Snapshot-Dependent Components . After confirming that the components are correct, run the following command to update the snapshot CRD. If controller.snapshot.enabled is set to false or the Kubernetes version is earlier than v1.20, you can skip this step. For details, see Table 2 .
kubectl apply -f ./crds/snapshot-crds/ --validate=falseRun the following command to install Huawei CSI. In the preceding command, helm-huawei-csi indicates the custom Helm chart name, ./ indicates that the Helm project in the current directory is used, and huawei-csi indicates the custom Helm chart namespace.
helm install helm-huawei-csi ./ -n huawei-csi --create-namespaceThe following is an example of the command output.
NAME: helm-huawei-csi LAST DEPLOYED: Wed Jun 8 11:50:28 2022 NAMESPACE: huawei-csi STATUS: deployed REVISION: 1 TEST SUITE: NoneAfter the huawei-csi service is deployed, run the following command to check whether the service is started.
kubectl get pod -n huawei-csiThe following is an example of the command output. If the Pod status is Running, the installation is successful.
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE huawei-csi-controller-6dfcc4b79f-9vjtq 9/9 Running 0 24m huawei-csi-controller-6dfcc4b79f-csphc 9/9 Running 0 24m huawei-csi-node-g6f4k 3/3 Running 0 20m huawei-csi-node-tqs87 3/3 Running 0 20m
Installation and Configuration on the OpenShift Platform
For the OpenShift platform, perform the following steps to create the SecurityContextConstraints resource.
Run the following command to edit the helm_scc.yaml file.
vi helm_scc.yamlModify the helm_scc.yaml file. In the following commands, huawei-csi indicates the created namespace. Replace it based on the actual situation.
apiVersion: security.openshift.io/v1 kind: SecurityContextConstraints metadata: name: helm-scc allowHostDirVolumePlugin: true allowHostIPC: true allowHostNetwork: true allowHostPID: true allowHostPorts: true allowPrivilegeEscalation: true allowPrivilegedContainer: true defaultAddCapabilities: - SYS_ADMIN runAsUser: type: RunAsAny seLinuxContext: type: RunAsAny fsGroup: type: RunAsAny users: - system:serviceaccount:huawei-csi:huawei-csi-controller - system:serviceaccount:huawei-csi:huawei-csi-nodeRun the following command to create a SecurityContextConstraints file.
oc create -f helm_scc.yaml
Installation and Configuration on the Tanzu Platform
On the Tanzu platform, run the following command to configure the kubelet installation directory.
Go to the helm/esdk directory in the installation package, and run the following command to open the configuration file. For details about the installation package directory, see Table 1 .
vi values.yamlModify the kubeletConfigDir parameter as follows and save the settings.
# Specify kubelet config dir path. # kubernetes and openshift is usually /var/lib/kubelet # Tanzu is usually /var/vcap/data/kubelet # CCE is usually /mnt/paas/kubernetes/kubelet kubeletConfigDir: /var/vcap/data/kubelet
For TKGI 1.16 or earlier of the Tanzu platform, run the following commands to configure the RBAC permission.
Run the following command to create a file named rbac.yaml.
vi rbac.yamlCopy the following content to the rbac.yaml file, save the file, and exit.
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: ClusterRole metadata: name: huawei-csi-psp-role rules: - apiGroups: ['policy'] resources: ['podsecuritypolicies'] verbs: ['use'] --- apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: ClusterRoleBinding metadata: name: huawei-csi-psp-role-cfg roleRef: kind: ClusterRole name: huawei-csi-psp-role apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io subjects: - kind: Group apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io name: system:serviceaccounts:huawei-csi - kind: Group apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io name: system:serviceaccounts:defaultRun the following command to create the RBAC permission.
kubectl create -f rbac.yaml
1.2.1.2 - Installing Huawei CSI on the CCE or CCE Agile Platform
This section describes how to install Huawei CSI on the CCE or CCE Agile platform.
Creating a Helm Installation Package
The CCE or CCE Agile platform cannot directly install Huawei CSI using Helm. You need to manually create a Helm installation package and upload it to the chart list on the platform for installation.
Use a remote access tool, such as PuTTY, to log in to any node where Helm is deployed through the management IP address.
Copy the helm directory in the Huawei CSI component package to any directory on the node. For details about the Helm tool path, see Table 1 .
Go to the helm working directory.
cd helm/Modify the kubeletConfigDir and csiDriver.driverName parameters in the helm/esdk/values.yaml file.
vi ./esdk/values.yamlModify the following parameters:
# Specify kubelet config dir path. # kubernetes and openshift is usually /var/lib/kubelet # Tanzu is usually /var/vcap/data/kubelet # CCE is usually /mnt/paas/kubernetes/kubelet kubeletConfigDir: /mnt/paas/kubernetes/kubelet # The CSI driver parameter configuration csiDriver: # Driver name, it is strongly recommended not to modify this parameter # The CCE platform needs to modify this parameter, e.g. csi.oceanstor.com driverName: csi.oceanstor.comRun the following command to create a Helm installation package. This command will generate the installation package to the current path.
helm package ./esdk/ -d ./
Installing Huawei CSI
Use a remote access tool, such as PuTTY, to log in to any master node where the CCE Agile platform is deployed through the management IP address.
Run the following command to create a namespace for deploying Huawei CSI. huawei-csi indicates the custom namespace.
kubectl create namespace huawei-csiExport the Helm installation package. For details, see Creating a Helm Installation Package .
On the home page, choose Charts > My Charts > Upload Chart. The Upload Chart dialog box is displayed. Import the exported Helm installation package to the CCE Agile platform.
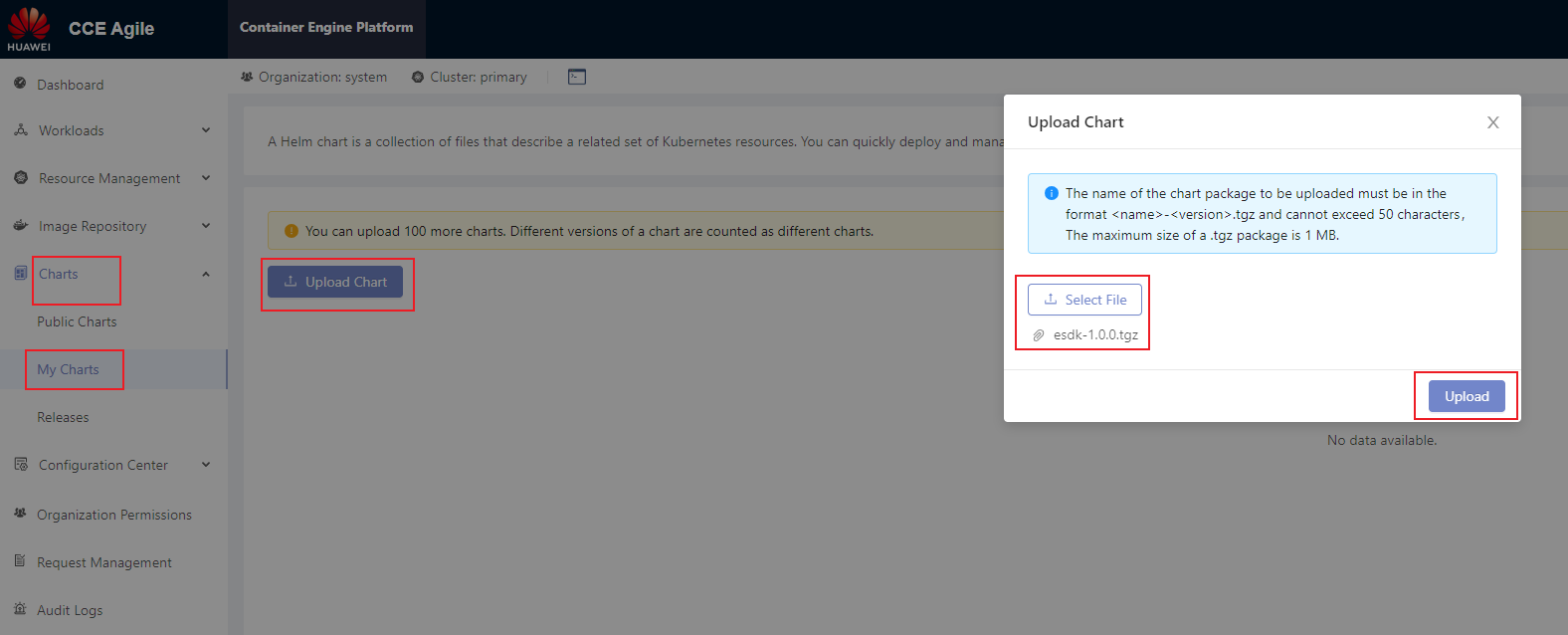
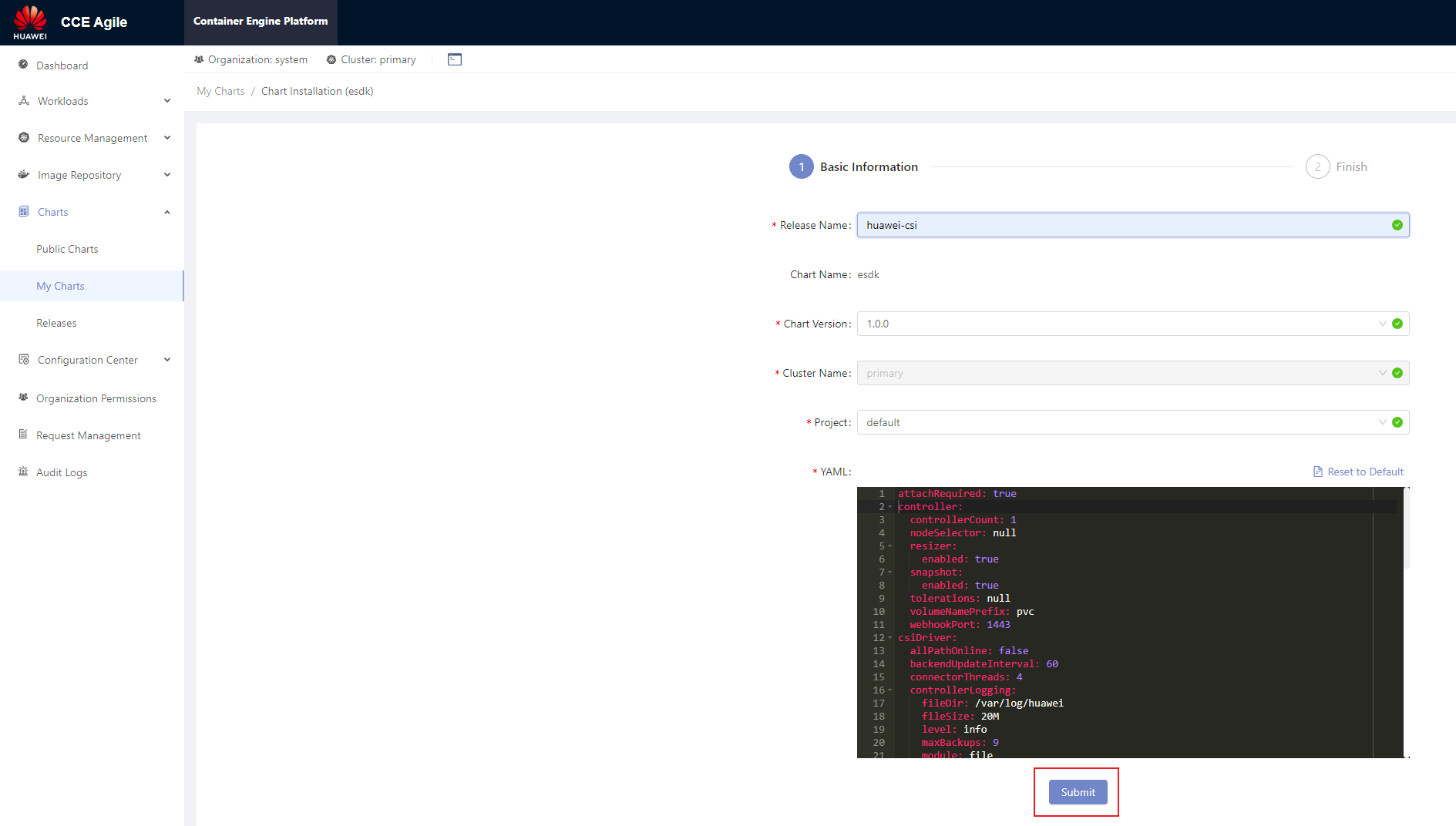
After the installation package is uploaded, choose Charts > My Charts. On the My Charts page that is displayed, choose Install > Submit. The chart release name can be customized.
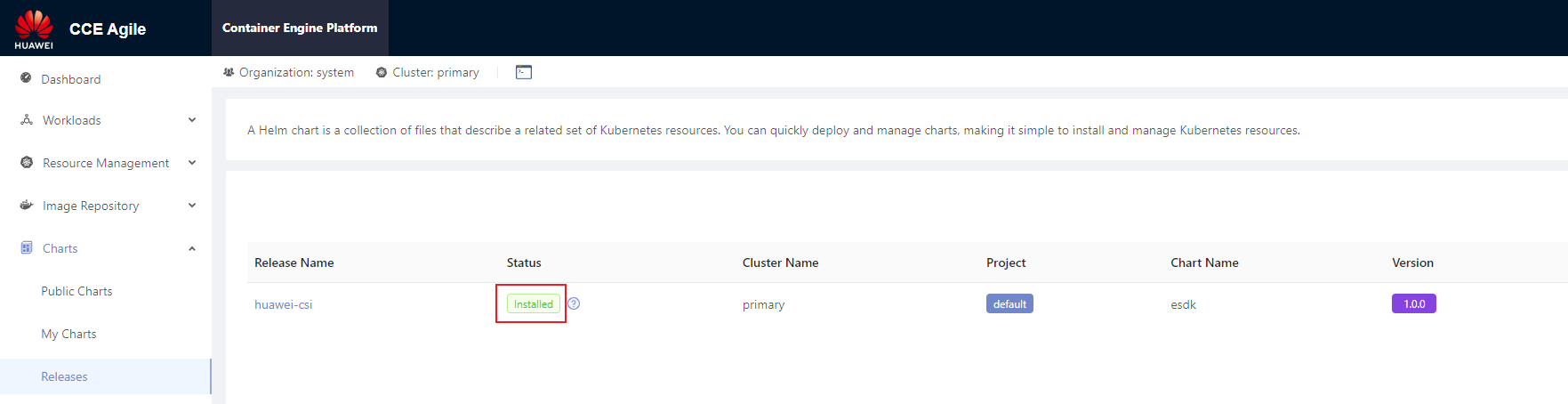
On the home page, choose Charts > Releases and select the project specified during installation (for example, default in the following figure). After the installation is successful, Installed is displayed in the Status column.
1.2.1.3 - Parameters in the values.yaml File of Helm
When using Helm to install CSI, you need to prepare the values.yaml file of the Helm project based on the features required during deployment. Huawei CSI provides the values.yaml template file in the helm/esdk directory of the software package.
This section describes the configuration items in the values.yaml file and backend configuration examples in typical scenarios.
images Parameters
The images parameters in the values.yaml file are used to configure the component image information on which Huawei CSI depends during running. Set the following parameters:
Table 1 images parameters
livenessprobe sidecar image. | |||
csi-provisioner sidecar image. | |||
csi-attacher sidecar image. | |||
csi-resizer sidecar image. | |||
csi-snapshotter sidecar image. | |||
snapshot-controller sidecar image. | |||
csi-node-driver-registrar sidecar image. | registry.k8s.io/sig-storage/csi-node-driver-registrar:v2.9.0 |
- For details about the values of huaweiCSIService, storageBackendSidecar, storageBackendController, and huaweiCSIExtender, see Uploading a Huawei CSI Image . Use the name and version of the finally generated image.
- For details about other sidecar image parameters, see Checking the Images on Which CSI Depends . Use the name and version of the finally uploaded image.
controller Parameters
The controller parameters are used to configure the huawei-csi-controller component.
Table 2 controller parameters
If the Kubernetes version is earlier than v1.17, the huawei-csi-controller component can be deployed only in single-copy mode because the csi-provisioner sidecar image provided by the Kubernetes community does not support the --leader-election parameter. Therefore, if the Kubernetes version is earlier than v1.17, this parameter can only be set to 1. | ||||
PV name prefix. The default value is pvc, that is, the name of a created PV is pvc-<uuid>. The prefix must comply with the naming rules of DNS Subdomain Names, and the total length of the PV name cannot exceed 253 characters. | The corresponding provisioner parameter name is --volume-name-prefix. It is recommended that the prefix contain no more than 20 characters. For details, see Configuring the PV Name Prefix.
| |||
If a port conflict occurs, change the port number to an idle one. | ||||
If you want to use snapshot-related functions, enable this feature. | ||||
Node selector of huawei-csi-controller. After this parameter is set, huawei-csi-controller will be scheduled only to a node with the label. | For details about the node selector, see Assign Pods to Nodes. | |||
Taint toleration of huawei-csi-controller. After this parameter is set, huawei-csi-controller can tolerate taints on a node. | For details about taints and tolerations, see Taints and Tolerations. | |||
Node affinity of huawei-csi-controller. After this parameter is set, huawei-csi-controller will be preferentially scheduled to a node with the label. | For details about node affinity, see Assigning Pods to Nodes. | |||
Liveness probe port of huawei-csi-controller, used for health check. | If a port conflict occurs, change the port number to an idle one. | |||
If you want to use PVC change-related functions, enable this feature. | ||||
Minimum retry interval when a PVC change fails to be created. | ||||
Maximum retry interval when a PVC change fails to be created. | ||||
Whether to run CSI services on the Service of the Kubernetes cluster. | After this function is enabled, other services in the Kubernetes cluster can access CSI services through gRPC. | |||
Port used when CSI services run on the Service of the Kubernetes cluster. | If a port conflict occurs, change the port number to an idle one. |
If controller.snapshot.enabled is set to true, you need to install the volume snapshot CRD resource in the helm/crd/snapshot-crds directory.
node Parameters
The node parameters are used to configure the huawei-csi-node component.
Table 3 node parameters
Maximum number of volumes provisioned by Huawei CSI that can be used by a node. If this parameter is not specified or is set to 0, the number is unlimited. If nodeName is specified during Pod creation, this configuration will be ignored. | For details, see Volume Limits. | |||
Node selector of huawei-csi-node. After this parameter is set, huawei-csi-node will be scheduled only to a node with the label. | For details about the node selector, see Assign Pods to Nodes. | |||
Taint toleration of huawei-csi-node. After this parameter is set, huawei-csi-node can tolerate taints on a node. | - key: "node.kubernetes.io/memory-pressure" operator: "Exists" effect: "NoExecute" - key: "node.kubernetes.io/disk-pressure" operator: "Exists" effect: "NoExecute" - key: "node.kubernetes.io/network-unavailable" operator: "Exists" effect: "NoExecute" | For details about taints and tolerations, see Taints and Tolerations. | ||
Node affinity of huawei-csi-node. After this parameter is set, huawei-csi-node will be preferentially scheduled to a node with the label. | For details about node affinity, see Assigning Pods to Nodes. | |||
Liveness probe port of huawei-csi-node, used for health check. | If a port conflict occurs, change the port number to an idle one. | |||
Name of the directory where a block device is mounted to kubelet. | After a block device is successfully mounted, the directory structure of the mount path is as follows: /var/lib/kubelet/plugins/kubernetes.io/csi/{kubeletVolumeDevicesDirName}/publish/{specName}/{podUID} |
csiDriver Parameters
The csiDriver parameters include the basic configurations for running Huawei CSI, such as Huawei driver name and multipathing type.
Table 4 csiDriver parameters
If Huawei CSI has been deployed in your container environment, ensure that the value of csiDriver.driverName is the same as that configured during previous deployment. Otherwise, existing volumes or snapshots provisioned by Huawei CSI in the system cannot be managed by the newly deployed Huawei CSI.
Other Parameters
Other parameters include some features of the CSI plug-in or the policies for obtaining images.
Table 5 Other parameters
Kubernetes namespace where Huawei CSI is running, which can be customized. The name must consist of lowercase letters, digits, and hyphens (-), for example, my-name and 123-abc. | ||||
Used by the Kubernetes cluster to pass the identity authentication of an image registry to pull private images. | For details, see Pull an Image from a Private Registry. | |||
The CSIDriver feature is a GA version in Kubernetes v1.18. Therefore, to use this feature, the Kubernetes version must be later than v1.18. If the Kubernetes version is earlier than v1.18, set this parameter to false. | ||||
Whether the CSI plug-in skips the attach operation. The following parameter values can be configured: | The attachRequired parameter can be configured in Kubernetes v1.18. If CSIDriverObject.isCreate is set to true and attachRequired is set to false, the huawei-csi plug-in will not deploy the csi-attacher sidecar. | |||
Whether the ownership and permissions of a basic volume can be changed before the volume is mounted. The following parameter values can be configured:
| The fsGroupPolicy parameter can be configured in Kubernetes v1.20, and takes effect only when CSIDriverObject.isCreate is set to true. This feature is a Beta version in Kubernetes v1.20 but a GA version in Kubernetes v1.23. Therefore, the Kubernetes version must be later than v1.20. | |||
This parameter takes effect only in the multi-controller scenario. | ||||
This parameter takes effect only in the multi-controller scenario. | ||||
This parameter takes effect only in the multi-controller scenario. | ||||
| ||||
| ||||
You can allocate container resources related to huawei-csi-controller and huawei-csi-node: resources.<component>.<container-name> <component> supports the following values:
controller.<container-name> supports the following values:
node.<container-name> supports the following values:
| For the default values of different container resources, see Huawei CSI Resource Management. | The following uses livenessProbe of huawei-csi-controller as an example: resources: controller: limits: cpu: 100m memory: 128Mi requests: cpu: 10m memory: 128Mi |
Ensure that the namespace entered in kubernetes.namespace exists on Kubernetes. If the namespace does not exist, run the following command to create it. In this example, the namespace for running Huawei CSI is huawei-csi.kubectl create namespace huawei-csi
1.2.2 - Manual Installation
This section describes how to manually install Huawei CSI.
Currently, only the Kubernetes platform supports manual installation of Huawei CSI.
Procedure
Use a remote access tool, such as PuTTY, to log in to any master node in the cluster through the management IP address.
Copy the manual directory in the Kubernetes CSI component package to any directory on the master node.
Run the following command to create a namespace. huawei-csi is used as an example namespace.
kubectl create ns huawei-csiGo to the manual/esdk working directory. For details about the path, see Table 1 .
cd manual/esdkRun the following command to update the storage backend CRD.
kubectl apply -f ./crds/backend/(Optional) Check snapshot-dependent components by following the instructions provided in Checking Volume Snapshot-Dependent Components . After confirming that the components are correct, run the following command to update the snapshot CRD. If the Kubernetes version is earlier than v1.20, skip this step.
kubectl apply -f ./crds/snapshot-crds/ --validate=false(Optional) Run the following command to install CSIDriver. If the CSIDriver feature is not used, you can skip this step. For details, see the CSIDriver feature.
kubectl apply -f ./deploy/csidriver.yamlRun the following command to install the huawei-csi-controller service.

If the Kubernetes version is earlier than v1.20, modify the ./deploy/huawei-csi-controller.yaml file as follows:- If the Kubernetes version is earlier than v1.20, the snapshot feature is not supported. In this case, delete the snapshot-related container configurations items csi-snapshotter and snapshot-controller. If the Kubernetes version is earlier than v1.17, modify the ./deploy/huawei-csi-controller.yaml file as follows:
- If the Kubernetes version is earlier than v1.17, the snapshot feature is not supported. In this case, delete the snapshot-related container configurations items csi-snapshotter and snapshot-controller.
- If the Kubernetes version is earlier than v1.17, the csi-provisioner sidecar image provided by the Kubernetes community does not support the –leader-election parameter. Therefore, the leader-election parameter of the csi-provisioner container is deleted and only single-copy deployment is supported.
- Modify the dependent image version based on the version requirements in Checking the Images on Which CSI Depends .
kubectl apply -f ./deploy/huawei-csi-controller.yamlRun the following command to install the huawei-csi-node service.
kubectl apply -f ./deploy/huawei-csi-node.yamlRun the following command to check whether the services are started.
kubectl get pod -n huawei-csiThe following is an example of the command output. If the Pod status is Running, the installation is successful.
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE huawei-csi-controller-68745d489c-v5xkj 9/9 Running 0 13m huawei-csi-node-4hbqp 3/3 Running 0 13m huawei-csi-node-f7dkf 3/3 Running 0 13m huawei-csi-node-xrntc 3/3 Running 0 13m
In the multi-copy controller deployment scenario, you can modify the spec.replica field of the Deployment resource in the ./deploy/huawei-csi-controller.yaml file to specify the number of copies. After the modification, run the kubectl apply -f ./deploy/huawei-csi-controller.yaml command to make the configuration take effect.
1.3 - Uninstallation
This section describes how to uninstall Huawei CSI. The uninstallation method varies according to the installation mode.
If you do not uninstall Huawei CSI for the purpose of an upgrade, ensure that all resources (such as PV, PVC, snapshot, and storage backend resources) provisioned by Huawei CSI have been cleared on your container platform before uninstalling Huawei CSI. Otherwise, once you uninstall Huawei CSI, these resources cannot be automatically scheduled, managed, or cleared.
1.3.1 - Uninstallation Using Helm
1.3.1.1 - Uninstalling Huawei CSI on Kubernetes, OpenShift, and Tanzu
This section describes how to uninstall Huawei CSI on the Kubernetes, OpenShift, and Tanzu platforms.
Procedure
Use a remote access tool, such as PuTTY, to log in to any master node in the Kubernetes cluster through the management IP address.
Run the following command to uninstall Huawei CSI. In the command, helm-huawei-csi indicates the custom Helm chart name and huawei-csi indicates the namespace where the Helm chart resides. This command will uninstall the huawei-csi-controller, huawei-csi-node, and RBAC resources of Huawei CSI.
helm uninstall helm-huawei-csi -n huawei-csiAfter the uninstallation command is executed, you need to check whether the uninstallation is successful. In the preceding command, huawei-csi indicates the namespace where the chart is located.
helm list -n huawei-csiThe following is an example of the command output. If the command output is empty, the service is successfully uninstalled.
NAME NAMESPACE REVISION UPDATED STATUS CHART APP VERSIONUninstall the huawei-csi-host-info object. For details, see Uninstalling the huawei-csi-host-info Object .
Uninstall the webhook resource. For details, see Uninstalling a Webhook Resource .
(Optional) Uninstall the snapshot-dependent component service. For details, see Uninstalling the Snapshot-Dependent Component Service .
(Optional) Uninstall the Lease resource. For details, see Uninstalling a Lease Resource .
(Optional) Run the following command to delete the namespace where Huawei CSI is located. The default namespace huawei-csi is used as an example.
kubectl delete ns huawei-csi
1.3.1.2 - Uninstalling Huawei CSI on CCE or CCE Agile
This section describes how to uninstall Huawei CSI on the CCE or CCE Agile platform. The following uses CCE Agile v22.3.2 as an example.
Procedure
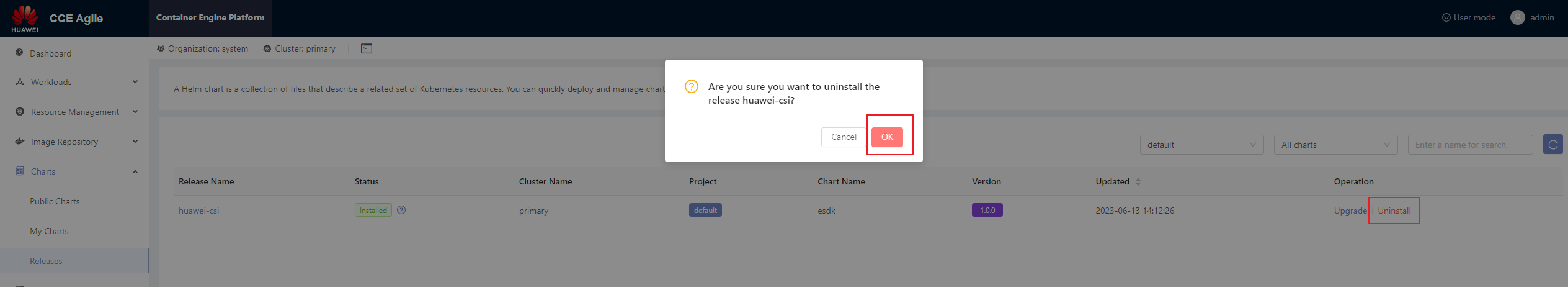
Log in to the CCE Agile platform.
On the home page, choose Charts > Releases. The Releases page is displayed.
Select a Huawei CSI release and click Uninstall. In the displayed dialog box, click OK.
Uninstall the huawei-csi-host-info object. For details, see Uninstalling the huawei-csi-host-info Object .
Uninstall the webhook resource. For details, see Uninstalling a Webhook Resource .
(Optional) Uninstall the snapshot-dependent component service. For details, see Uninstalling the Snapshot-Dependent Component Service .
(Optional) Run the following command to delete the namespace where Huawei CSI is located. huawei-csi is used as an example namespace.
kubectl delete ns huawei-csi
1.3.1.3 - Uninstalling CSI-Dependent Component Services
This section describes how to uninstall the CSI-dependent component services.
Uninstalling the huawei-csi-host-info Object
Secret object huawei-csi-host-info stores the initiator information about each node in the cluster, for example, iSCSI initiators. When you run the helm uninstall command, the resource will not be uninstalled. To uninstall the resource, perform the following steps:
Use a remote access tool, such as PuTTY, to log in to any master node in the Kubernetes cluster through the management IP address.
Run the following command to delete the Secret object. huawei-csi-host-info is the name of the Secret object, and huawei-csi is the namespace where the Secret object is located.
kubectl delete secret huawei-csi-host-info -n huawei-csiRun the following command to check whether the Secret object is successfully uninstalled.
kubectl get secret huawei-csi-host-info -n huawei-csiThe following is an example of the command output. If NotFound is displayed in the command output, the huawei-csi-host-info object is successfully uninstalled.
Error from server (NotFound): secrets "huawei-csi-host-info" not found
Uninstalling a Webhook Resource
The webhook resource named storage-backend-controller.xuanwu.huawei.io is used to verify the backend key information and connectivity with the storage. When you run the helm uninstall command, the resource will not be uninstalled. To uninstall the resource, perform the following steps:
Use a remote access tool, such as PuTTY, to log in to any master node in the Kubernetes cluster through the management IP address.
Run the following command to query the webhook-dependent component service.
kubectl get validatingwebhookconfigurations.admissionregistration.k8s.io storage-backend-controller.xuanwu.huawei.ioThe following is an example of the command output.
NAME WEBHOOKS AGE storage-backend-controller.xuanwu.huawei.io 1 12dRun the following command to uninstall the webhook-dependent component service.
kubectl delete validatingwebhookconfigurations.admissionregistration.k8s.io storage-backend-controller.xuanwu.huawei.ioRun the following command to check whether the service is successfully uninstalled. If the command output is empty, the uninstallation is successful.
kubectl get validatingwebhookconfigurations.admissionregistration.k8s.io storage-backend-controller.xuanwu.huawei.io
Uninstalling the Snapshot-Dependent Component Service
- Do not uninstall the snapshot-dependent component service when snapshots exist. Otherwise, Kubernetes will automatically delete all user snapshots and they cannot be restored. For details, see Delete a CustomResourceDefinition .
- Do not uninstall the snapshot-dependent component service during the CSI upgrade.
Scenario Description
- Currently, Huawei CSI uses the snapshot feature.
- Currently, only Huawei CSI is available in the Kubernetes cluster, and Huawei CSI is no longer used.
- Before the uninstallation, ensure that no VolumeSnapshot resource managed by Huawei CSI exists in the Kubernetes cluster.
Procedure
Use a remote access tool, such as PuTTY, to log in to any master node in the Kubernetes cluster through the management IP address.
Run the following command to uninstall the snapshot-dependent component service.
kubectl delete crd volumesnapshotclasses.snapshot.storage.k8s.io volumesnapshotcontents.snapshot.storage.k8s.io volumesnapshots.snapshot.storage.k8s.ioRun the following command to check whether the service is successfully uninstalled. If the command output is empty, the uninstallation is successful.
kubectl get crd | grep snapshot.storage.k8s.io
Uninstalling a Lease Resource
When huawei-csi-controller is deployed in multi-copy mode, a Lease resource is generated to store the current Holder information. When you run the helm uninstall command, the resource will not be uninstalled. To uninstall the resource, perform the following steps:
Use a remote access tool, such as PuTTY, to log in to any master node in the Kubernetes cluster through the management IP address.
Run the following command to query the Lease information.
kubectl get lease -n huawei-csiThe following is an example of the command output.
NAME HOLDER AGE csi-huawei-com node-1 24d external-attacher-leader-csi-huawei-com node-1 24d external-resizer-csi-huawei-com node-1 24d external-snapshotter-leader-csi-huawei-com node-1 24d snapshot-controller-leader node-1 24d storage-backend-controller node-1 24d huawei-csi-extender node-1 24dRun the following command to uninstall the Lease resource.
kubectl delete lease -n huawei-csi csi-huawei-com external-attacher-leader-csi-huawei-com external-resizer-csi-huawei-com external-snapshotter-leader-csi-Run the following command to check whether the uninstallation is successful.
kubectl get lease -n huawei-csiThe following is an example of the command output. If the command output is empty, the uninstallation is successful.
No resources found in huawei-csi namespace.
1.3.2 - Manual Uninstallation
This section describes how to manually uninstall Huawei CSI.
If you do not uninstall Huawei CSI for the purpose of an upgrade, ensure that all resources (such as PV, PVC, snapshot, and storage backend resources) provisioned by Huawei CSI have been cleared on your container platform before uninstalling Huawei CSI. Otherwise, once you uninstall Huawei CSI, these resources cannot be automatically scheduled, managed, or cleared.
Uninstalling the huawei-csi-node Service
Use a remote access tool, such as PuTTY, to log in to any master node in the Kubernetes cluster through the management IP address.
Run the following command to uninstall the huawei-csi-node service. Replace huawei-csi with the namespace where Huawei CSI is located.
kubectl delete daemonset huawei-csi-node -n huawei-csiRun the following command to check whether the service is successfully uninstalled. If NotFound is displayed, the service is successfully uninstalled.
kubectl get daemonset huawei-csi-node -n huawei-csi
Uninstalling the huawei-csi-controller Service
Use a remote access tool, such as PuTTY, to log in to any master node in the Kubernetes cluster through the management IP address.
Run the following command to uninstall the huawei-csi-controller service. Replace huawei-csi with the namespace where Huawei CSI is located.
kubectl delete deployment huawei-csi-controller -n huawei-csiRun the following command to check whether the service is successfully uninstalled. If NotFound is displayed, the service is successfully uninstalled.
kubectl get deployment huawei-csi-controller -n huawei-csi
Uninstalling the csidriver Object
If the CSIDriver feature is not used during installation , you can skip the following steps.
Use a remote access tool, such as PuTTY, to log in to any master node in the Kubernetes cluster through the management IP address.
Run the following command to uninstall the csidriver object.
kubectl delete csidriver csi.huawei.comRun the following command to check whether the service is successfully uninstalled. If NotFound is displayed, the service is successfully uninstalled.
kubectl get csidriver csi.huawei.com
Deleting the RBAC Permission
Use a remote access tool, such as PuTTY, to log in to any master node in the Kubernetes cluster through the management IP address.
Delete the RBAC permission.
kubectl -n huawei-csi -l provisioner=csi.huawei.com delete ServiceAccount,Service,role,rolebinding,ClusterRole,ClusterRoleBinding
Uninstalling Other Resources
Uninstall the huawei-csi-host-info object. For details, see Uninstalling the huawei-csi-host-info Object .
Uninstall the webhook resource. For details, see Uninstalling a Webhook Resource .
(Optional) Uninstall the snapshot-dependent component service. For details, see Uninstalling the Snapshot-Dependent Component Service .
(Optional) Uninstall the Lease resource. For details, see Uninstalling a Lease Resource .
(Optional) Run the following command to delete the namespace where Huawei CSI is located. The default namespace huawei-csi is used as an example.
kubectl delete ns huawei-csi
1.4 - Upgrade
This section describes how to upgrade Huawei CSI.
In the current version, resource requests and limits are added to Huawei CSI. For details, see Huawei CSI Resource Management .
1.4.1 - Upgrade Using Helm
This section describes how to upgrade Huawei CSI.
- To upgrade Huawei CSI from 2.x to 4.10.0, uninstall it by referring to the user guide of the earlier version and install Huawei CSI by referring to Installation Using Helm .
- To upgrade Huawei CSI from 2.x or 3.x to 4.10.0, see Upgrading from 2.x or 3.x to 4.x .
- To upgrade Huawei CSI from 4.x to 4.10.0, see Upgrading Huawei CSI on Kubernetes, OpenShift, and Tanzu .
- Some CSI 2.x versions are unavailable now. If the upgrade fails, CSI may fail to be rolled back to a version which is unavailable now.
- After an upgrade from 2.x, 3.x, or 4.x to 4.10.0, a Pod that has been provisioned in the source version may fail to be mounted again. For details, see Upgrading from 2.x or 3.x to 4.x .
- During the upgrade or rollback, you cannot use Huawei CSI to create new resources or mount or unmount an existing PVC.
- During the upgrade or rollback, do not uninstall the snapshot-dependent component service.
- During the upgrade or rollback, the existing resources such as PVCs, snapshots, and Pods will run properly and will not affect your service access.
1.4.1.1 - Upgrading from 2.x or 3.x to 4.x
In CSI 2.x or 3.x, when block storage is used, the mapping with storage is set up in the huawei-csi-node service. Therefore, the huawei-csi-node service needs to communicate with the storage management network. Because the huawei-csi-node service is deployed as a DaemonSet, the huawei-csi-node service is deployed on each node in the cluster. As a result, in a large-scale cluster, each huawei-csi-node service sends requests to the storage and the number of storage connections may be fully occupied. Accordingly, huawei-csi-node cannot provide services properly. In CSI 4.x, the deployment model is optimized. The setup of the mapping with storage is migrated to the huawei-csi-controller service and the huawei-csi-node service does not need to communicate with the storage management network. This reduces the networking complexity of Huawei CSI. In addition, the huawei-csi-controller service is deployed as a Deployment. The number of copies is set based on the customer’s reliability requirements. Generally, the number of copies ranges from 1 to 3. Therefore, the number of connections between Huawei CSI and storage is greatly reduced, so that Huawei CSI can connect to a large-scale cluster. This change may cause a problem. That is, if a new mount process is generated after CSI is upgraded to 4.x but with workloads provisioned using 2.x or 3.x and the Container Orchestration (CO) system does not invoke the huawei-csi-controller service provided by Huawei CSI, the mounting will fail. For details, see A Pod Fails to Be Created and Message “publishInfo doesn’t exist” Is Displayed in the Events Log .
To upgrade Huawei CSI from 2.x or 3.x to 4.x, perform following operations.
Backing Up Storage Backend Configurations
If you have evaluated the risks mentioned in the preceding notice and need to upgrade CSI from 2.x or 3.x to 4.10.0, perform the following steps to back up storage backend configurations:
Use a remote access tool, such as PuTTY, to log in to any master node in the Kubernetes cluster through the management IP address.
Run the following command to back up the backend information to the configmap.json file. For the OpenShift platform, replace kubectl with oc.
kubectl get cm huawei-csi-configmap -n huawei-csi -o json > configmap.json
Upgrading Huawei CSI
Perform the upgrade according to the procedure described in Upgrading Huawei CSI .
Configuring the Storage Backend
Configure the storage backend by following the instructions in Storage Backend Management according to the backend information backed up in Backing Up Storage Backend Configurations . After the storage backend is successfully configured, perform operations according to the risk handling methods described in the preceding notice to prevent problems during Pod failover.
1.4.1.2 - Upgrading Huawei CSI on Kubernetes, OpenShift, and Tanzu
Prerequisites
- Huawei CSI of an earlier version is installed using Helm.
- A Huawei CSI image of a new version has been created and uploaded to the image repository or imported to all nodes by following the instructions provided in Uploading a Huawei CSI Image .
Upgrading Huawei CSI
If CSI of an earlier version is deployed using Helm, perform the following steps to upgrade Huawei CSI.
Use a remote access tool, such as PuTTY, to log in to any master node in the Kubernetes cluster through the management IP address.
Copy the CSI component package of the target version to any directory on the master node.
Go to the helm/esdk working directory. For the directory path, see Table 1 .
cd helm/esdkRun the kubectl apply -f ./crds/backend/ command to update the storage backend CRD.
kubectl apply -f ./crds/backend/(Optional) Check snapshot-dependent components by following the instructions provided in Checking Volume Snapshot-Dependent Components . After confirming that the components are correct, run the following command to update the snapshot CRD. If controller.snapshot.enabled is set to false or the Kubernetes version is earlier than v1.20, you can skip this step. For details, see Table 2 .
kubectl apply -f ./crds/snapshot-crds/ --validate=falseRun the following command to obtain the original service configuration file. helm-huawei-csi indicates the Helm chart name specified during the installation of the earlier version, and huawei-csi indicates the Helm chart namespace specified during the installation of the earlier version.
helm get values helm-huawei-csi -n huawei-csi -a > ./update-values.yamlRun the vi update-values.yaml command to open the file obtained in 6 , modify the images configuration items, and update the image to the latest version. For details about the parameters to be modified, see Table 1 .
Table 1 images configuration items
Image used by Huawei backends to manage storageBackendContent resources.
Image used by Huawei backends to manage storageBackendClaim resources.
livenessprobe sidecar image.
csi-resizer sidecar image.
csi-node-driver-registrar sidecar image.
registry.k8s.io/sig-storage/csi-node-driver-registrar:v2.9.0
csi-snapshotter sidecar image.
snapshot-controller sidecar image.
csi-provisioner sidecar image.
csi-attacher sidecar image.
(Optional) If you need to update configuration items or add configuration information during the upgrade, modify the configuration information in the update-values.yaml file by referring to Parameters in the values.yaml File of Helm .

During the upgrade, if the update-values.yaml and values.yaml configuration files contain the same configuration item, the configuration in the update-values.yaml file takes effect preferentially.Run the following command to upgrade Huawei CSI. In the following command, helm-huawei-csi indicates the specified Helm chart name, huawei-csi indicates the specified Helm chart namespace, and update-values.yaml indicates the file obtained in 6 .
helm upgrade helm-huawei-csi ./ -n huawei-csi -f ./values.yaml -f ./update-values.yamlAfter the huawei-csi service is deployed, run the following command to check whether the service is started.
kubectl get pod -n huawei-csiThe following is an example of the command output. If the Pod status is Running, the service is started successfully.
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE huawei-csi-controller-6dfcc4b79f-9vjtq 9/9 Running 0 24m huawei-csi-controller-6dfcc4b79f-csphc 9/9 Running 0 24m huawei-csi-node-g6f4k 3/3 Running 0 20m huawei-csi-node-tqs87 3/3 Running 0 20m
1.4.1.3 - Upgrading Huawei CSI on CCE or CCE Agile
Prerequisites
You have downloaded the CSI software package of a new version.
Procedure
- Uninstall CSI. For details, see Uninstalling Huawei CSI on CCE or CCE Agile .
- Install CSI of the new version. For details, see Installing Huawei CSI on the CCE or CCE Agile Platform .
1.4.2 - Manual Upgrade
This section describes how to manually upgrade Huawei CSI.
During the upgrade or rollback, the existing resources such as PVCs, snapshots, and Pods will run properly and will not affect your service access.
- Some CSI 2.x versions are unavailable now. If the upgrade fails, CSI may fail to be rolled back to a version which is unavailable now.
- During the upgrade or rollback, you cannot use Huawei CSI to create new resources or mount or unmount an existing PVC.
- During the upgrade or rollback, do not uninstall the snapshot-dependent component service.
Upgrading CSI from 2.x or 3.x to 4.10.0
To upgrade CSI from 2.x or 3.x to 4.10.0, perform the following operations:
Use a remote access tool, such as PuTTY, to log in to any master node in the Kubernetes cluster through the management IP address.
Run the following command to back up the backend information to the configmap.json file. For the OpenShift platform, replace kubectl with oc.
kubectl get cm huawei-csi-configmap -n huawei-csi -o json > configmap.jsonUninstall CSI. For details, see Manual Uninstallation .
Install CSI of the current version. For details, see Manual Installation .
Install the backend information backed up in 2 according to Storage Backend Management .
Upgrading CSI from 4.x to 4.10.0
To upgrade CSI from 4.x to 4.10.0, perform the following operations:
- Use a remote access tool, such as PuTTY, to log in to any master node in the Kubernetes cluster through the management IP address.
- Uninstall CSI. For details, see Manual Uninstallation .
- Install CSI of the current version. For details, see Manual Installation .
1.5 - Rollback
1.5.1 - Rollback Using Helm
If CSI fails to be upgraded from 2.x or 3.x to 4.10.0 and needs to be rolled back, uninstall CSI by referring to Uninstallation Using Helm and then download and install CSI of the source version.
- During the upgrade or rollback, the existing resources such as PVCs, snapshots, and Pods will run properly and will not affect your service access.
- During the upgrade or rollback, you cannot use Huawei CSI to create new resources or mount or unmount an existing PVC.
- During the upgrade or rollback, do not uninstall the snapshot-dependent component service.
1.5.1.1 - Rolling Back Huawei CSI on Kubernetes, OpenShift, and Tanzu
Prerequisites
- CSI has been updated using Helm 3.
Procedure
Use a remote access tool, such as PuTTY, to log in to any master node in the Kubernetes cluster through the management IP address.
Go to the helm/esdk working directory. For the directory path, see Table 1 .
cd helm/esdkRun the following command to query the historical versions of the CSI services deployed using Helm.
helm history helm-huawei-csi -n huawei-csiThe following is an example of the command output.
REVISION UPDATED STATUS CHART APP VERSION DESCRIPTION 1 Mon Jan 8 04:15:40 2024 superseded esdk-4.4.0 4.4.0 Install complete 2 Mon Jan 8 04:16:12 2024 deployed esdk-4.10.0 4.10.0 Upgrade completeRun the following command to roll back the CSI services to the specified version.
In the preceding command, revision-number indicates a version number queried in 3 . For example, the version is 1.
helm rollback helm-huawei-csi -n huawei-csi 1The following is an example of the command output. If Rollback was a success is displayed in the command output, the CSI services are successfully rolled back to the specified version.
Rollback was a success! Happy Helming!
1.5.1.2 - Rolling Back Huawei CSI on CCE or CCE Agile
- During the upgrade or rollback, the existing resources such as PVCs, snapshots, and Pods will run properly and will not affect your service access.
- During the upgrade or rollback, you cannot use Huawei CSI to create new resources or mount or unmount an existing PVC.
- During the upgrade or rollback, do not uninstall the snapshot-dependent component service.
Prerequisites
You have downloaded the CSI software package of the source version.
Procedure
- Use a remote access tool, such as PuTTY, to log in to any master node in the Kubernetes cluster through the management IP address.
- Uninstall CSI. For details, see Procedure .
- Reinstall CSI of the source version. For details, see Installing Huawei CSI on the CCE or CCE Agile Platform .
1.5.2 - Manual Rollback
Uninstall CSI by referring to Manual Uninstallation , and then download and install CSI of the source version.
- During the upgrade or rollback, the existing resources such as PVCs, snapshots, and Pods will run properly and will not affect your service access.
- During the upgrade or rollback, you cannot use Huawei CSI to create new resources or mount or unmount an existing PVC.
- During the upgrade or rollback, do not uninstall the snapshot-dependent component service.
Prerequisites
You have downloaded the CSI software package of the source version.
Procedure
- Use a remote access tool, such as PuTTY, to log in to any master node in the Kubernetes cluster through the management IP address.
- Uninstall CSI. For details, see Manual Uninstallation .
- Reinstall CSI of the source version. For details, see Manual Installation .