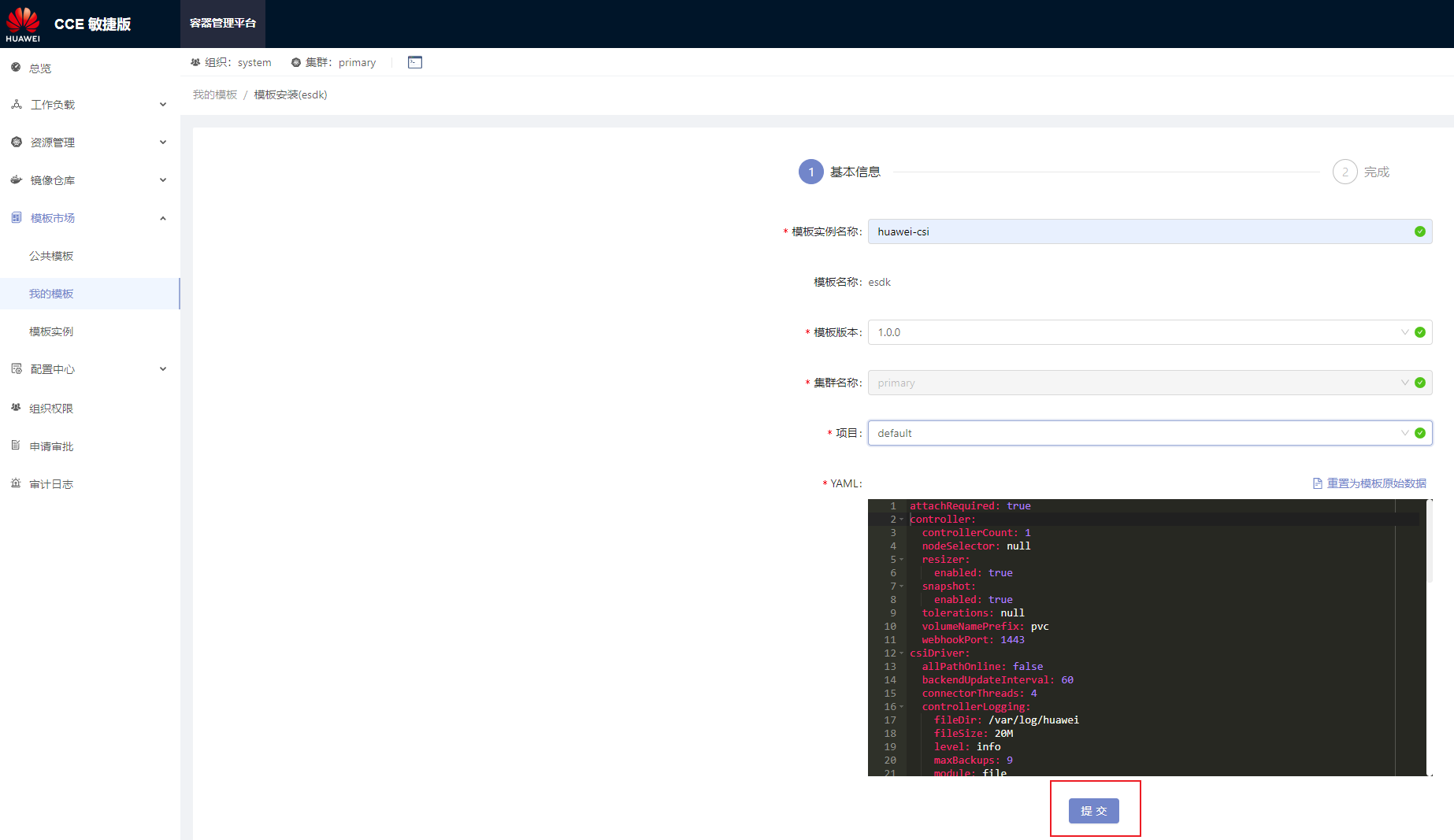
csiDriver.driverName | Registered driver name. | Yes | csi.huawei.com | - Use the default value.
- For the CCE Agile platform, modify this field. For example, csi.oceanstor.com.
|
csiDriver.endpoint | Communication endpoint. | Yes | /csi/csi.sock | Use the default value. |
csiDriver.connectorThreads | Maximum number of disks that can be concurrently scanned/detached. The value is an integer ranging from 1 to 10. | Yes | 4 | A larger value indicates that more concurrent disk scanning and detaching operations are performed on a single node at the same time. When DM-Multipath is used, a large number of concurrent requests may cause unknown problems and affect the overall time. |
csiDriver.volumeUseMultipath | Whether to use multipathing software. The value is a Boolean value. | Yes | true | It is strongly recommended that multipathing software be enabled to enhance the redundancy and performance of storage links. |
csiDriver.scsiMultipathType | Multipathing software used when the storage protocol is fc or iscsi. The following parameter values can be configured: - DM-multipath
- HW-UltraPath
- HW-UltraPath-NVMe
| Mandatory when volumeUseMultipath is set to true. | DM-multipath | The DM-multipath value is recommended. |
csiDriver.nvmeMultipathType | Multipathing software used when the storage protocol is roce or fc-nvme. Only HW-UltraPath-NVMe is supported. | Mandatory when volumeUseMultipath is set to true. | HW-UltraPath-NVMe | - |
csiDriver.scanVolumeTimeout | Timeout interval for waiting for multipathing aggregation when DM-Multipath is used on the host. The value ranges from 1 to 600 seconds. | Yes | 3 | - |
csiDriver.execCommandTimeout | Timeout interval for running commands on the host. | Yes | 30 | In scenarios such as mounting and capacity expansion, the CSI plug-in needs to run some host commands, for example, running the mount command to mount a file system. This parameter is used to control the timeout interval for running a single command. |
csiDriver.enableRoCEConnect | Whether to enable automatic disk scanning for CSI when the RoCE protocol is used. | No | true | If an external tool is used to establish RoCE connections, you can set this parameter to false. For example, if the SNSD automatic connection function is enabled on storage devices, you can set this parameter to false. |
csiDriver.allPathOnline | Whether to check whether the number of paths aggregated by DM-Multipath is equal to the actual number of online paths. The following parameter values can be configured: - true: The drive letter mounting condition is met only when the number of paths aggregated by DM-Multipath is equal to the actual number of online paths.
- false: By default, the number of paths aggregated by DM-Multipath is not checked. As long as virtual drive letters are generated upon aggregation, the drive letter mounting condition is met.
| This parameter is mandatory when csiDriver.scsiMultipathType is set to DM-multipath. | false | - |
csiDriver.backendUpdateInterval | Interval for updating backend capabilities. The value ranges from 60 to 600 seconds. | Yes | 60 | - |
csiDriver.controllerLogging.module | Record type of the controller log. The following parameter values can be configured: | Yes | file | When the value is file, logs are retained in the specified directory of the node. When the Pod where CSI is located is destroyed, logs are still retained. When the value is console, logs are retained in the temporary space of the Pod where CSI is located. When the Pod where CSI is located is destroyed, the logs are also destroyed. |
csiDriver.controllerLogging.level | Output level of the controller log. The following parameter values can be configured: - debug
- info
- warning
- error
- fatal
| Yes | info | - |
csiDriver.controllerLogging.fileDir | Directory of the controller log in file output mode. | Yes | /var/log/huawei | Ensure that the directory has sufficient space for storing logs. It is recommended that the space be greater than or equal to 200 MB. |
csiDriver.controllerLogging.fileSize | Size of a single controller log file in file output mode. | Yes | 20M | - |
csiDriver.controllerLogging.maxBackups | Maximum number of controller log file backups in file output mode. | Yes | 9 | - |
csiDriver.nodeLogging.module | Record type of the node log. The following parameter values can be configured: | Yes | file | When the value is file, logs are retained in the specified directory of the node. When the Pod where CSI is located is destroyed, logs are still retained. When the value is console, logs are retained in the temporary space of the Pod where CSI is located. When the Pod where CSI is located is destroyed, the logs are also destroyed. |
csiDriver.nodeLogging.level | Output level of the node log. The following parameter values can be configured: - debug
- info
- warning
- error
- fatal
| Yes | info | - |
csiDriver.nodeLogging.fileDir | Directory of the node log in file output mode. | Yes | /var/log/huawei | Ensure that the directory has sufficient space for storing logs. It is recommended that the space be greater than or equal to 200 MB. |
csiDriver.nodeLogging.fileSize | Size of a single node log file in file output mode. | Yes | 20M | - |
csiDriver.nodeLogging.maxBackups | Maximum number of node log file backups in file output mode. | Yes | 9 | - |