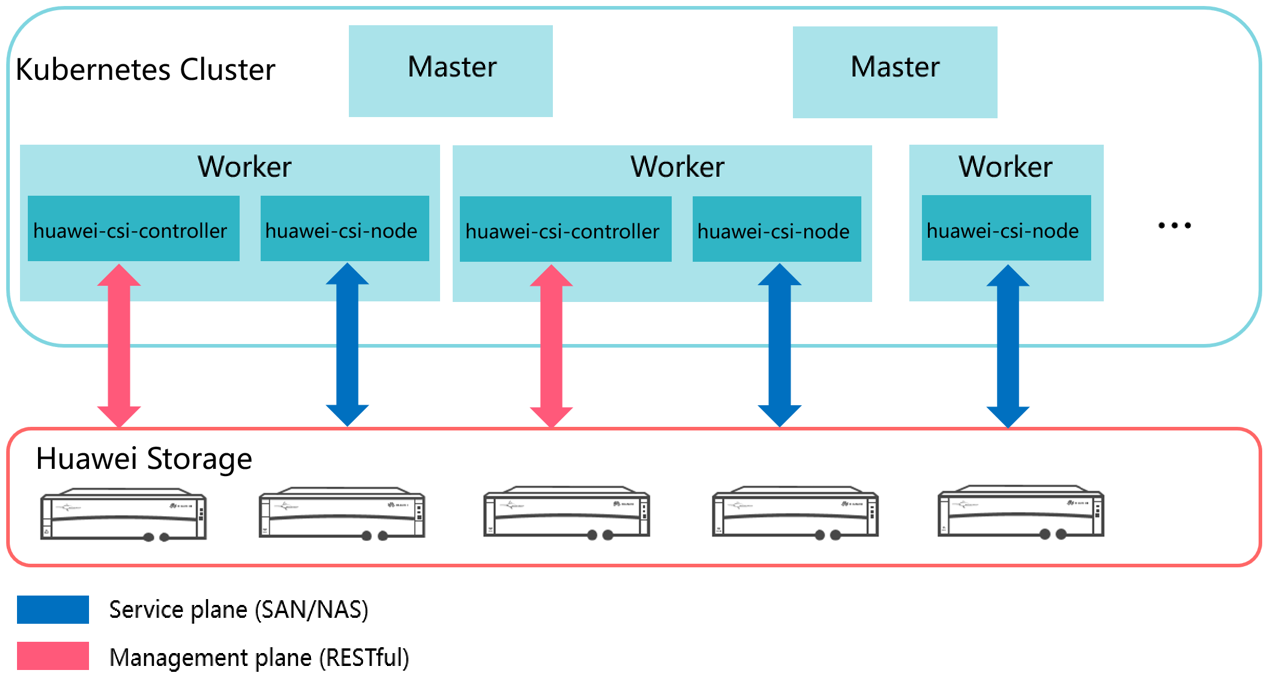
Container Storage Interface (CSI) is an industry standard protocol used to connect container platforms such as Kubernetes to underlying storage systems. Huawei CSI is a mandatory component that connects Huawei enterprise storage and distributed storage products to Kubernetes clusters, providing persistent storage services for containerized workload.
Kubernetes uses a series of officially maintained sidecar components to register and listen Kubernetes object resources and invoke the CSI driver to trigger physical operations on Huawei storage. For example, when a Persistent Volume (PV) is created, the Huawei CSI driver creates a LUN (block storage) or file system on the storage device. Figure 1 shows the overall structure of Kubernetes, Huawei CSI, and Huawei storage.
Figure 1 CSI overall architecture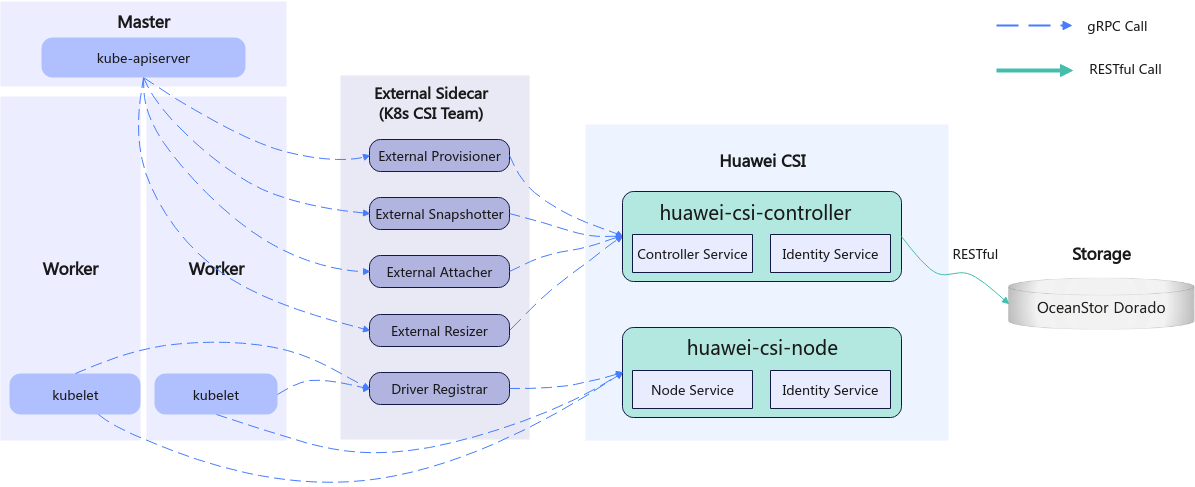
Huawei CSI consists of two components: huawei-csi-controller and huawei-csi-node.
- huawei-csi-controller: one or more Pods (including Controller Service and Identity Service) running in Deployment mode. It is used to interact with Huawei storage using RESTful. Therefore, the node running the huawei-csi-controller component must be connected to the management plane network of the storage.
- huawei-csi-node: a Pod (including Node Service and Identity Service) that runs on Kubernetes worker nodes in DaemonSet mode. It is used to mount and unmount a LUN/file system provided by Huawei storage on worker nodes. Therefore, the node running the huawei-csi-node component must be connected to the service plane network of the storage.
Figure 2 shows the deployment model of Huawei CSI.
This document describes how to install, deploy, and use the Huawei CSI V4.10.0 plug-in.